Is It True When You Are in the Whom You Are a Girl at Fridt Then You Can Become a Noy
The Showtime Trimester
What You Need to Know
- At your offset prenatal visit, you will undergo a concrete examination equally well equally certain tests and screenings to assess the health of yous and your unborn baby.
- Outset trimester symptoms vary from adult female to adult female, with some experiencing all known symptoms and others only a few. Duration of symptoms can vary every bit well.
- After eight weeks, the embryo is referred to as a fetus.
- Although the fetus is only ane to 1.five inches long at this point, all major organs and systems have been formed.
- During the first trimester, the fetus is nigh susceptible to damage from substances, like booze, drugs and certain medicines, and illnesses, like rubella (German measles).
Your Outset Prenatal Visit
Your first prenatal visit is the almost thorough. A consummate medical history is taken, a physical exam is done, and certain tests and procedures are performed to appraise the health of both yous and your unborn infant. Your kickoff prenatal visit may include:
-
Personal medical history. This may include taking record of any of the following:
-
Previous and current medical conditions, like diabetes, high claret pressure (hypertension), anemia and/or allergies
-
Current medicines (prescription, over-the-counter and nutritional supplements)
-
Previous surgeries
-
-
Maternal and paternal family unit medical history, including illnesses, intellectual or developmental disabilities, and genetic disorders, like sickle prison cell disease or Tay-Sachs disease
-
Personal gynecological and obstetrical history, including past pregnancies (stillbirths, miscarriages, deliveries, terminations) and menstrual history (length and duration of menstrual periods)
-
Education, including a discussion regarding the importance of proper nutrition and expected weight gain in pregnancy; regular exercise; the avoidance of booze, drugs and tobacco during pregnancy; and a discussion of any concerns nearly domestic violence
-
Pelvic test. This exam may be done for one or all of the post-obit reasons:
-
To notation the size and position of the uterus
-
To make up one's mind the historic period of the fetus
-
To check the pelvic os size and structure
-
To perform a Pap test (also called Pap smear) to detect the presence of aberrant cells
-
-
Lab tests, including the following:
-
Urine tests. These are done to screen for bacteria, glucose and protein.
-
Claret tests. These are done to determine your claret type.
-
All pregnant women are tested for the Rh factor during the early weeks of pregnancy. Rh incompatibility happens when the mother'due south blood is Rh-negative, the father's claret is Rh-positive and the fetus' blood is Rh-positive. The mother may make antibodies confronting the Rh-positive fetus, which may atomic number 82 to anemia in the fetus. Incompatibility problems are watched and appropriate medical treatment is available to prevent the germination of Rh antibodies during pregnancy. There are as well other blood antibodies that may cause problems in pregnancy that are screened for on the start visit.
-
-
-
Claret screening tests. These are washed to find diseases that could have an outcome on the pregnancy. One instance is rubella, an infectious disease that is also chosen High german measles.
-
Genetic tests. These are done to find inherited diseases, like sickle cell illness and Tay-Sachs disease.
-
Other screening tests. These are performed to find infectious diseases, similar sexually transmitted diseases and urinary tract infections.
The first prenatal visit is also an opportunity to inquire any questions or discuss any concerns that you may have about your pregnancy.
The First Trimester: What to Look
A healthy start trimester is crucial to the normal development of the fetus. Yous may not exist showing much on the exterior yet, merely on the inside, all of the major body organs and systems of the fetus are forming.
As the embryo implants itself into the uterine wall, several developments take place, including the formation of the:
-
Amniotic sac. A sac filled with amniotic fluid, called the amniotic sac, surrounds the fetus throughout the pregnancy. The amniotic fluid is liquid fabricated past the fetus and the amnion (the membrane that covers the fetal side of the placenta) that protects the fetus from injury. It also helps to regulate the temperature of the fetus.
-
Placenta. The placenta is an organ shaped similar a flat cake that only grows during pregnancy. It attaches to the uterine wall with tiny projections called villi. Fetal blood vessels grow from the umbilical cord into these villi, exchanging nourishment and waste products with your blood. The fetal blood vessels are separated from your blood supply by a thin membrane.
-
Umbilical cord. The umbilical cord is a ropelike cord connecting the fetus to the placenta. The umbilical cord contains two arteries and a vein, which comport oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and waste products abroad from the fetus.
It is during this first trimester that the fetus is nigh susceptible to damage from substances, like alcohol, drugs and certain medicines, and illnesses, like rubella (German measles).
During the beginning trimester, your body and your infant's body are changing chop-chop.

Johns Hopkins Hospital Designated equally Baby-Friendly
The Infant-Friendly Hospital Initiative, a global plan launched by the World Health Organization and the United nations Children's Fund, has designated The Johns Hopkins Hospital equally Babe-Friendly. This designation is given to hospitals and birthing centers that offer an optimal level of intendance for infant feeding and mother-babe bonding.
The Commencement Trimester: Changes to Your Body
During pregnancy, many changes will happen to your body to assist nourish and protect your baby. Women experience these changes differently. Some symptoms of pregnancy continue for several weeks or months. Others are only experienced for a short time. Some women experience many symptoms, and other women feel but a few or none at all. The following is a list of changes and symptoms that may happen during the first trimester:
-
The mammary glands enlarge, causing the breasts to swell and become tender in training for breast-feeding. This is due to an increased amount of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. A supportive bra should be worn.
-
Your areolas (the pigmented areas around each breast'south nipple) volition enlarge and darken. They may go covered with small-scale, white bumps called Montgomery's tubercles (enlarged sweat glands).
-
Veins become more noticeable on the surface of your breasts.
-
The uterus is growing and begins to press on your float. This causes you to need to urinate more oftentimes.
-
Partly due to surges in hormones, you may feel mood swings like to premenstrual syndrome, a condition experienced by some women that is characterized by mood swings, irritability and other physical symptoms that happen presently before each menstrual period.
-
Increased levels of hormones to sustain the pregnancy may cause "morning sickness," which causes nausea and sometimes airsickness. However, morning sickness does not necessarily happen just in the morning and rarely interferes with proper diet for the mother and her fetus.
-
Constipation may happen as the growing uterus presses on the rectum and intestines.
-
The muscular contractions in the intestines, which assistance to motility food through the digestive tract, are slowed due to high levels of progesterone. This may, in plough, cause heartburn, indigestion, constipation and gas.
-
Apparel may experience tighter around the breasts and waist, equally the size of the stomach begins to increase to accommodate the growing fetus.
-
You may experience extreme tiredness due to the concrete and emotional demands of pregnancy.
-
Cardiac volume increases past about twoscore to 50 percent from the get-go to the end of the pregnancy. This causes an increased cardiac output. An increased cardiac output may cause an increased pulse rate during pregnancy. The increase in blood volume is needed for actress blood flow to the uterus.
The Outset Trimester: Fetal Development
The most dramatic changes and evolution happen during the first trimester. During the get-go 8 weeks, a fetus is called an embryo. The embryo develops apace and by the end of the first trimester, it becomes a fetus that is fully formed, weighing approximately 0.5 to ane ounce and measuring, on average, 3 to 4 inches in length.
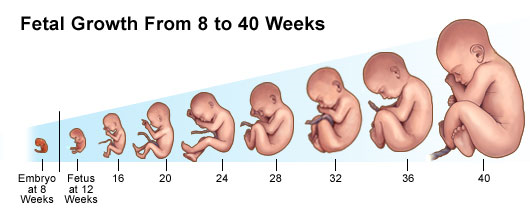
First Trimester Fetal Growth and Development Benchmarks
The chart beneath provides benchmarks for nearly normal pregnancies. However, each fetus develops differently.
| Timing | Development Benchmark |
|---|---|
| Past the end of four weeks |
|
| Past the end of eight weeks |
|
| From embryo to fetus |
|
| During weeks nine to 12 |
|
The fetus is most vulnerable during the first 12 weeks. During this period of time, all of the major organs and body systems are forming and can be damaged if the fetus is exposed to drugs, infectious agents, radiation, certain medications, tobacco and toxic substances.
Even though the organs and trunk systems are fully formed by the end of 12 weeks, the fetus cannot survive independently.
skeltondrebeguing70.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-first-trimester
0 Response to "Is It True When You Are in the Whom You Are a Girl at Fridt Then You Can Become a Noy"
Post a Comment